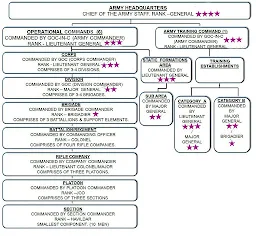
STRUCTURE OF ARMY
The Indian army has strength of about a million troops and fields 34 divisions. Its headquarters is located in the Indian capital New Delhi and it is under the overall command of the Chief of Army Staff (COAS).
Formation and Structure of Indian Army
Command: Indian Army has 6 operational commands and 1 training command. Each one is headed by a General Officer Commanding-in-Chief (GOC-in-C), known as Army Commander, who is among the senior-most Lieutenant General officers in the army. Each command is directly affiliated to the Army HQ in New Delhi. There is also the Army Training Commanded abbreviated as ARTRAC.
The Andaman and Nicobar Command is the first and only Tri-service theater command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Corps: A command generally consists of two or more corps. Indian Army has 13 Corps & each one is commanded by a General Officer Commanding (GOC), known as Corps Commander, who holds the rank of Lieutenant General. Each corps is composed of 3–4 Divisions. There are three types of corps in the Indian Army: Strike, Holding and Mixed. The Corps HQ is the highest field formation in the army.
- I Corps – Mathura (Uttar Pradesh)
- II Corps – Ambala (Haryana)
- III Corps – Dimapur (Nagaland)
- IV Corps – Tezpur (Asom)
- IX Corps – Dharamsala (Himachal Pradesh)
- X Corps – Bhatinda (Punjab)
- XI Corps – Jalandhar (Punjab)
- XII Corps – Jodhpur (Rajasthan)
- XIV Corps – Leh (J & K)
- XV Corps – Srinagar (J & K)
- XVI Corps – Nagrota (J & K)
- XXI Corps – Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh)
- XXXIII Corps – Siliguri (West Bengal)
- Division: Each Division is headed by General Officer Commanding (GOC) in the rank of Major General. It usually consists of 15,000 combat troops and 8,000 support elements. Currently, the Indian Army has 37 Divisions including; 4 RAPID (Re-organized Army Plains Infantry Divisions) Action Divisions, 18 Infantry Divisions, 10 Mountain Divisions, 3 Armored Divisions and 2 Artillery Divisions. Each Division composes of several Brigades.
- Brigade: A Brigade generally consists of around 3,000 combat troops with supporting elements. An Infantry Brigade usually has 3 Infantry Battalions along with various Support Arms & Services. It is headed by a Brigadier. In addition to the Brigades in various Army Divisions, the Indian Army also has 5 Independent Armored Brigades, 15 Independent Artillery Brigades, 7 Independent Infantry Brigades, 1 Independent Parachute Brigade,3 Independent Air Defence Brigades, 2 Independent Air Defence Groups and 4 Independent Engineer Brigades. These Independent Brigades operate directly under the Corps Commander (GOC Corps).
- Battalion: A Battalion is commanded by a Colonel and is the Infantry’s main fighting unit. It consists of more than 900 combat personnel.
- Company: Headed by the Major or Captain, a company comprises 120 soldiers.
- Platoon: An intermediate between a company and section, a platoon is headed by a Captain or Lieutenant, or depending on the availability of commissioned officers, even a junior commissioned officer (Subedar). It has a total strength of about 32 troops.
- Section: Smallest military outfit with a strength of 10 personnel. Commanded by a non-commissioned officer of the rank of Havildar or Sergeant.
- Buddy pair: Buddy pair are two individual who works as a pair, do everything together and have so much trust in each other that In Para SF, training is on the concept of a buddy system. For deadly missions, one needs to have great combat skills and tremendous trust in buddy. For trust exercises, they have to pass a Confidence Firing Test in which real bullets are used.








0 Comments